
















5,000 years ago, the world was experiencing a great time for the birth of civilizations. Early civilizations were born simultaneously in several major river basins of the world, such as the ancient Egyptian civilization in the Nile Valley, the Sumerian civilization in Mesopotamia, and the Harappan civilization in the Indus River Valley. Like the Liangzhu civilization, these civilizations all had a relatively stable industry model and complex social organization structure, mastered advanced engineering technical knowledge, and built large-scale projects such as cities and water conservancy systems. Together with the Liangzhu civilization, these civilizations have constituted a splendid galaxy of human civilization.
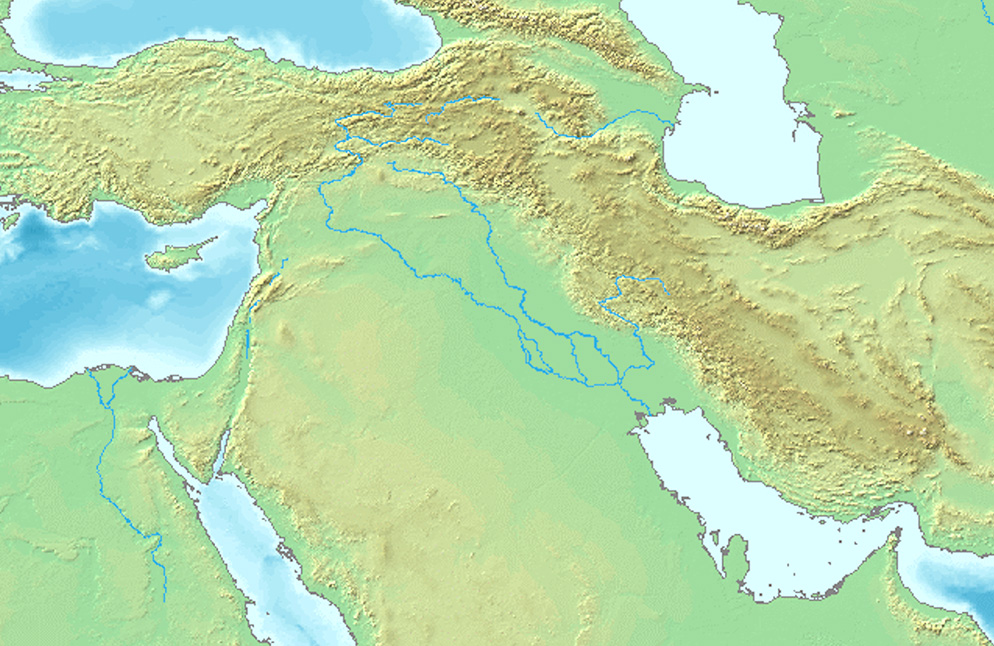
Sumer’s eneral location on a modern map. (CC BY-SA 3.0)

Anu ziggurat and White Temple at Uruk. (CC BY-SA 2.0)

The pyramids of Giza. (CC BY-SA 2.0)
The ancient Egyptian civilization lasted for nearly 3,000 years, from its formation as a unified kingdom in 3200 B.C. to its conquest by the Persians in 343 B.C. Ancient Egypt was a gift of the Nile, whose regular floods provided fertile soil for the ancient Egyptians to grow crops such as wheat and barley. Ancient Egypt had a complete writing system, political system and institutions, as well as a system of religious
belief in many gods and one lord. There were thirty successive dynasties on the land of Egypt, which together represented the journey forward of the Egyptians. The kings of Ancient Egypt built magnificent pyramid mausoleums for themselves, and the construction of pyramids also reflected the strong national power of kingdoms of Ancient Egypt.

Measuring and recording the harvest is shown in a wall painting in the tomb of Menna, at Thebes (Eighteenth Dynasty). (CC0)

A view of Harappa’s Granary and Great Hall. (CC BY-SA 3.0)
The Harappan civilization is the earliest known urban civilization on the Indian subcontinent. Its sites are mostly in present-day Pakistan, consisting of five cities, including Harappa and Mohenjo-daro, and more than 1,000 small towns and villages. The Harappan civilization is a widely distributed, far-reaching civilization with advanced urban planning and construction. The urbanization of Harappa began in 3300 B.C. and was fully urbanized around 2600 B.C., leading to the mature Harappan period, which lasted until about 1900 B.C. For more than 700 years, Harappa has been the largest and most powerful economic and political center in the Indus River Valley.
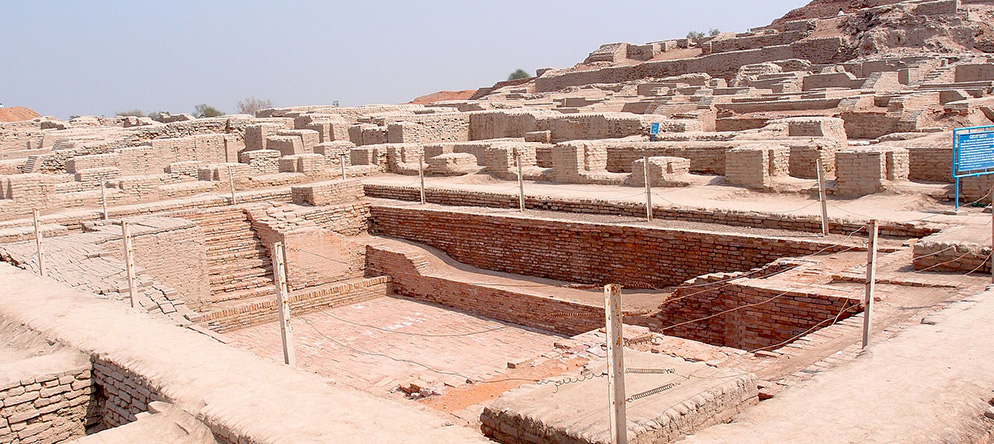

Excavated ruins of Mohenjo-daro, Sindh province, Pakistan
Harappa’s urban planning is very scientific and sophisticated, and its layout has been carefully designed. It has learned to use fired bricks to build houses which can be several stories high. The city has well-established public facilities, with wells in and around it to provide drinking water. It also has enormous granaries. This not only shows the affluence of the city at the time, but also marks the prosperity of civilization.